Financial Aid Packages: What to Expect When You Win a Scholarship

Landing a scholarship is an exciting achievement, offering financial support towards your educational goals. But what happens next? Understanding how scholarships interact with your overall financial aid package is crucial. This article explores the components of a typical financial aid package, including grants, loans, and work-study opportunities. We'll delve into how a scholarship impacts these elements, potentially reducing loan burdens or freeing up funds for living expenses. Discover how colleges adjust aid packages to reflect scholarship awards and learn strategies to navigate these changes effectively, ensuring you maximize your financial support and minimize debt.
Financial Aid Package Adjustments After Winning a Scholarship
Winning a scholarship is fantastic news, but it's crucial to understand how it affects your existing financial aid package. In most cases, your college's financial aid office will need to adjust your aid to account for the scholarship. This doesn't necessarily mean you'll lose aid altogether, but rather that the sources and amounts of aid might change. Typically, the scholarship will first reduce your unmet need, and then may impact other forms of aid, starting with self-help aid like loans and work-study, before touching grant aid. It is crucial to remember to communicate with the financial aid office about your scholarship details as soon as possible, so they can provide you with an updated financial aid package. Understanding the specifics of how your award impacts your aid is essential for effective financial planning.
How Scholarships Impact Your Unmet Need
Your "unmet need" is the difference between the cost of attendance (tuition, fees, room, board, etc.) and your Expected Family Contribution (EFC), as determined by the FAFSA. When you win a scholarship, the financial aid office will first use the scholarship amount to reduce your unmet need. If your scholarship is smaller than your unmet need, it might not affect other forms of aid. However, if the scholarship exceeds your unmet need, it will start to affect other components of your financial aid package.
Reduction of Loans and Work-Study
Typically, the financial aid office will reduce "self-help" aid such as student loans and work-study opportunities before reducing grants or scholarships offered directly by the institution. This is because loans need to be repaid, and work-study requires you to earn the money. A scholarship essentially lessens your need to borrow or work, so it's a logical first step in the adjustment process. Federal student loans are often reduced first, then potentially institutional loans, followed by work-study.
Impact on Grants and Institutional Aid
After loans and work-study are adjusted, the financial aid office may need to reduce grant aid. Federal Pell Grants and state grants are often protected to some extent, but institutional grants from the college itself may be reduced. The order in which aid is reduced depends on the institution's policies. It is important to check what those policies are. Keep in mind that the goal is to ensure you don't receive aid exceeding your cost of attendance.
Reporting Scholarship Information to the Financial Aid Office
As soon as you receive notification that you've won a scholarship, promptly inform the financial aid office at your college or university. Provide them with all the details, including the scholarship amount, any restrictions (like needing to maintain a certain GPA), and the disbursement schedule. Failure to report scholarships could lead to complications later, such as having your aid package adjusted retroactively or being required to repay funds.
Understanding Scholarship Displacement
Scholarship displacement is the practice of a college reducing its own grant aid by the amount of an outside scholarship. This means the student may not see the full financial benefit of winning a scholarship, as the college is essentially taking back some of its original offer. While controversial, it is a practice that some institutions use, especially those with limited financial resources. It is crucial to inquire about your college's policy on scholarship displacement to fully understand how your award will affect your overall aid package.
| Type of Aid | Likelihood of Reduction | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Loans | High | Scholarship reduces the need to borrow money. |
| Work-Study | High | Scholarship reduces the need to earn money through employment. |
| Institutional Grants | Medium | College may adjust its own grants to account for the scholarship. |
| Federal Grants (Pell) | Low | Federal grants are often protected but could be affected in extreme cases. |
| State Grants | Medium to Low | Similar to federal grants, state grants may be protected to a degree. |
What happens to my financial aid if I get a scholarship?

Reporting Your Scholarship
- It is crucial to promptly inform your financial aid office about any scholarship you receive, regardless of its size. Failure to report can result in complications or even the loss of financial aid. The financial aid office will guide you through the necessary documentation.
- Typically, they will require official documentation from the scholarship provider. This documentation should include the scholarship amount, the payment schedule, and any restrictions on the use of the funds.
- Make sure to keep copies of all submitted documents for your records. This proactive approach will ensure you have evidence of compliance and facilitates easy reference should any discrepancies arise.
The Impact on Need-Based Aid
- Need-based aid, such as Pell Grants, subsidized loans, and some institutional grants, is designed to cover the gap between the cost of attendance and your Expected Family Contribution (EFC). A scholarship reduces your financial need, which can lead to a reduction in need-based aid.
- The most common adjustment is a reduction in loan amounts. Your school may reduce your subsidized or unsubsidized loans to accommodate the scholarship. This can be beneficial in the long run as it decreases your debt burden after graduation.
- In some cases, the scholarship may reduce grant aid instead of or in addition to loans. The order in which aid is reduced typically depends on the school's policies. Some schools may prioritize reducing loan aid before reducing grant aid, while others may have different protocols.
The Impact on Non-Need-Based Aid
- Non-need-based aid, such as unsubsidized loans or merit-based scholarships, is not directly tied to your financial need. However, even non-need-based aid can be affected by a scholarship, although usually to a lesser extent. A scholarship might still impact the total amount of financial aid you can receive.
- Schools are required to ensure that your total financial aid package, including scholarships, does not exceed your Cost of Attendance (COA). If the combination of all aid sources exceeds your COA, adjustments must be made to bring the total within the limit.
- The reduction often targets loans, especially unsubsidized loans, as these do not directly correlate with your financial need. Grants may be reduced, but it is less common unless the aid package significantly exceeds the COA.
Scholarship Displacement
- Scholarship displacement refers to the practice where a college reduces its own institutional grant or scholarship when a student receives an external scholarship. This practice is controversial as it effectively diminishes the value of the external scholarship.
- Some institutions explicitly prohibit scholarship displacement, ensuring that external scholarships directly benefit the student by reducing loan debt or out-of-pocket expenses. Other institutions may allow scholarship displacement, reducing the student's institutional aid.
- The prevalence of scholarship displacement varies widely, and the policy is often disclosed on the college's website or in its financial aid materials. Check with your financial aid office to understand their specific policy on scholarship displacement.
Maximizing the Benefit of Your Scholarship
- In order to maximize the benefits of your scholarship, explore the possibility of using the funds to cover expenses not typically covered by financial aid, such as textbooks, transportation, or living expenses.
- If your scholarship leads to a reduction in loans, consider using the scholarship money to pay down any remaining loans you might have. This can significantly reduce your debt burden after graduation and save you money on interest.
- If your institution allows it, and your aid package significantly exceeds your cost of attendance, consider investing the scholarship funds in a savings account or a low-risk investment vehicle to grow your financial resources over time. Consult a financial advisor for personalized advice on investment strategies.
What happens after you win a scholarship?

Formal Acceptance and Paperwork
After receiving notification of your scholarship, the first step is typically to formally accept the award. This usually involves completing and returning paperwork to the scholarship provider. This paperwork might include:
- Acceptance Form: Confirming your intention to accept the scholarship and agreeing to the terms and conditions.
- Enrollment Verification: Proof that you are enrolled at the educational institution specified in the scholarship criteria.
- Tax Information: Providing necessary tax information for reporting purposes, as scholarship funds may be taxable depending on your country's regulations.
Understanding Scholarship Terms and Conditions
It's crucial to thoroughly understand the terms and conditions of the scholarship. This involves knowing the specifics of how the funds can be used, reporting requirements, and renewal criteria. Pay close attention to details such as:
- Eligible Expenses: Knowing exactly what expenses the scholarship covers (e.g., tuition, fees, books, room and board).
- Renewal Requirements: Understanding what you need to do to maintain the scholarship in subsequent years, such as maintaining a certain GPA.
- Reporting Requirements: Knowing what kind of academic progress reports or updates the scholarship provider requires during the scholarship period.
Financial Planning and Budgeting
Winning a scholarship can significantly ease the financial burden of education, but it's essential to incorporate it into your overall financial plan. This involves creating a budget and understanding how the scholarship funds will integrate with other sources of funding, such as loans or family contributions. Consider the following:
- Create a Budget: Develop a detailed budget that includes all your educational expenses and living costs.
- Track Expenses: Keep track of how you're spending your scholarship funds to ensure you stay within budget and meet any requirements.
- Explore Other Funding Options: If the scholarship doesn't cover all your expenses, look into other funding sources, such as grants or student loans.
Maintaining Academic Standards
Many scholarships require recipients to maintain a certain GPA or meet specific academic standards to remain eligible. Failing to meet these standards can result in the loss of the scholarship. This requires:
- Focus on Academics: Prioritize your studies and dedicate sufficient time to coursework.
- Seek Academic Support: Take advantage of tutoring services or academic advising if you're struggling in any subjects.
- Regularly Check Your GPA: Monitor your academic progress to ensure you're meeting the scholarship's GPA requirements.
Expressing Gratitude and Building Relationships
It's essential to express your gratitude to the scholarship provider. Sending a thank-you note or attending scholarship events can help build relationships with the organization and other recipients. This includes:
- Write a Thank-You Note: Express your appreciation for the scholarship and explain how it will help you achieve your educational and career goals.
- Attend Scholarship Events: If possible, attend any events organized by the scholarship provider to network and show your gratitude.
- Stay in Touch: Keep the scholarship provider updated on your academic progress and achievements throughout your educational journey.
What is the average financial aid package awarded?
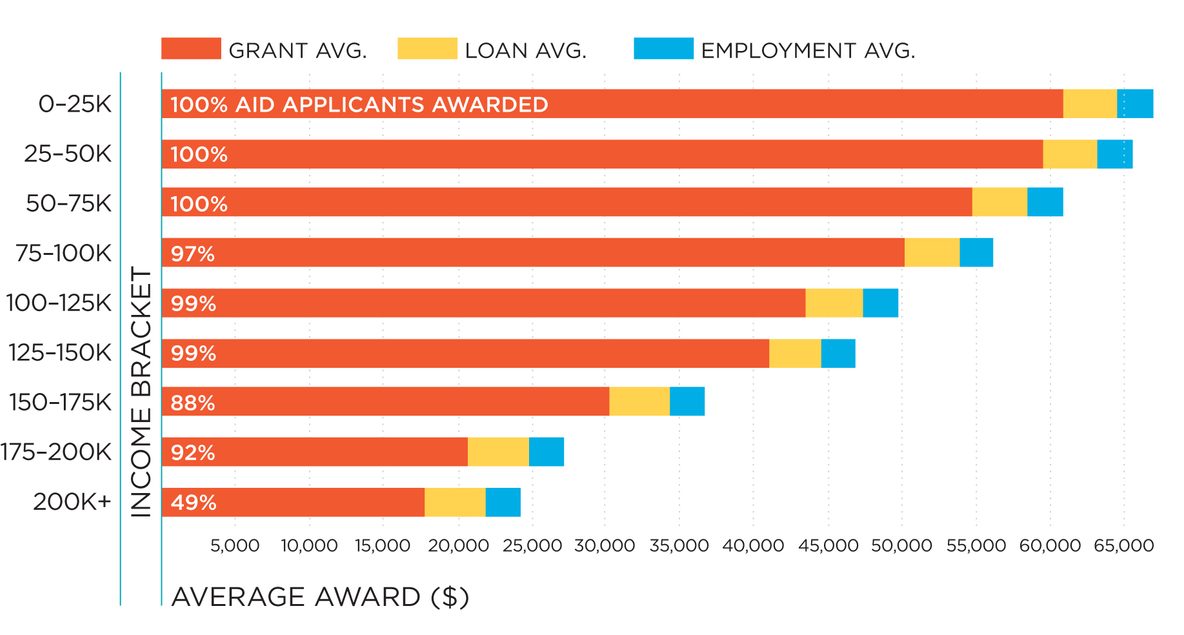
Factors Influencing Average Aid Amounts
- Type of Institution: Private colleges and universities often have higher tuition costs but also tend to offer more generous financial aid packages compared to public institutions. They rely heavily on endowments and private fundraising to supplement their financial aid budgets. Public institutions generally have lower tuition fees but may have more limited aid resources.
- EFC (Expected Family Contribution): The EFC, calculated based on the information provided in the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA), is a crucial determinant. Students with lower EFCs typically qualify for more need-based aid, including Pell Grants and subsidized loans.
- Merit-Based vs. Need-Based Aid: Some financial aid is awarded based on academic merit or other achievements, while other forms are based on financial need. Merit-based aid is often competitive and might not be directly tied to financial circumstances.
Components of a Typical Financial Aid Package
- Grants: These are typically need-based and do not need to be repaid. Common examples include Federal Pell Grants, state grants, and institutional grants. Grants often form a significant portion of the financial aid package for students with the greatest financial need.
- Scholarships: Scholarships can be awarded based on merit, talent, or specific criteria. They don't need to be repaid. Scholarship sources include colleges, private organizations, and foundations. Students should actively seek and apply for scholarships to reduce their reliance on loans.
- Loans: These must be repaid, usually with interest. Federal student loans, such as subsidized and unsubsidized loans, often have more favorable terms than private loans. It's essential to understand the repayment terms and interest rates before accepting a loan.
- Work-Study: This program allows students to earn money by working part-time jobs on campus or in approved off-campus organizations. It's designed to help students finance their education while gaining work experience.
Differences Between Public and Private Institution Aid
- Funding Sources: Public institutions receive funding from state governments, while private institutions rely more on tuition revenue, endowments, and donations. This difference in funding models affects the availability of financial aid. Private institutions generally have more flexibility in awarding aid and can offer larger packages.
- Tuition Costs: Tuition at private colleges and universities is usually significantly higher than at public institutions, so the amount of aid needed is typically larger. However, the aid packages also tend to be more comprehensive.
- Eligibility Criteria: The eligibility criteria for financial aid can vary slightly between public and private institutions. Some private colleges may use a more detailed assessment of a family's financial circumstances.
How to Maximize Your Financial Aid Potential
- Complete the FAFSA Early: Submitting the FAFSA as soon as it becomes available (October 1st) is crucial. Many financial aid programs have limited funding, and early applicants have a higher chance of receiving aid.
- Apply for Scholarships: Dedicate time to searching for and applying for scholarships. Numerous online resources and databases can help you find relevant scholarships. Tailor your applications to match the specific requirements of each scholarship.
- Negotiate with the Financial Aid Office: If you believe your financial aid package is insufficient, don't hesitate to contact the financial aid office. Be prepared to provide documentation to support your request. Situations like a recent job loss can impact financial aid eligibility.
- Consider Community College: Starting your education at a community college can significantly reduce costs. You can then transfer to a four-year university to complete your degree. This approach can save money on tuition and fees.
Resources for Finding More Information
- FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid): This is the primary application for federal student aid. It is used to determine eligibility for grants, loans, and work-study. The FAFSA website is a crucial resource.
- College Financial Aid Websites: Most colleges and universities have detailed information about their financial aid programs on their websites. Research the financial aid options available at each institution you are considering.
- Scholarship Search Engines: Websites like Sallie Mae, Scholarships.com, and Fastweb can help you find scholarships that match your qualifications and interests.
- College Board: The College Board offers various resources related to college planning and financial aid, including tools for estimating college costs and finding scholarships.
Frequently asked questions
What is a Financial Aid Package and How Does a Scholarship Affect It?
A financial aid package is a collection of grants, loans, and work-study opportunities designed to help students cover the cost of college. When you win a scholarship, it can affect your aid package because it reduces your "financial need." The college will typically reduce the amount of loans or grants in your package to account for the scholarship, meaning you'll borrow less money or receive fewer grant dollars.
Will My Scholarship Reduce My Grants or Loans?
Generally, your scholarship will first reduce the "self-help" portion of your aid package, which includes loans and work-study. If your scholarship is larger than the total amount of loans and work-study offered, it may then reduce your grant aid. It's important to contact your college's financial aid office to understand the specific impact on your award.
What Happens if My Scholarship Exceeds My Financial Need?
If the total value of your scholarships and other aid exceeds your assessed financial need, the college might reduce other forms of aid, such as institutional grants. In some cases, the college may even reduce the amount of your federal grants, although this is less common. Understanding your college's policies regarding over-awarding is crucial in these situations.
Can My Scholarship Impact My Expected Family Contribution (EFC)?
No, winning a scholarship does not directly impact your Expected Family Contribution (EFC). The EFC is calculated based on your family's financial information and is used to determine your financial need. A scholarship provides additional funding to meet that need, but it doesn't change the amount your family is expected to contribute according to the FAFSA.
