Scholarships vs. Loans: Which is the Best Financial Option?
Navigating the world of higher education often involves confronting a daunting financial reality. For many aspiring students, the question isn't simply *where* to study, but *how* to pay for it. Two primary options emerge: scholarships and loans. Both offer pathways to funding education, but they differ significantly in their implications. Scholarships represent "free money," awarded based on merit, need, or specific criteria. Loans, on the other hand, require repayment with interest. Understanding the nuances of each option is crucial. This article explores the differences between scholarships and loans, examining their advantages, disadvantages, and offering guidance on choosing the best financial path to achieving your educational goals.
Scholarships vs. Loans: Which is the Best Financial Option?
Deciding how to finance your education is a crucial step, and the choice between scholarships and loans can significantly impact your future financial well-being. Scholarships represent free money, requiring no repayment, while loans necessitate repayment with interest. Therefore, scholarships are generally the preferred option. However, securing enough scholarship funding to cover all educational expenses is often challenging, making loans a necessary consideration for many students. Understanding the nuances of both options is essential to making an informed decision that aligns with your financial circumstances and goals.
What are the Key Differences Between Scholarships and Loans?
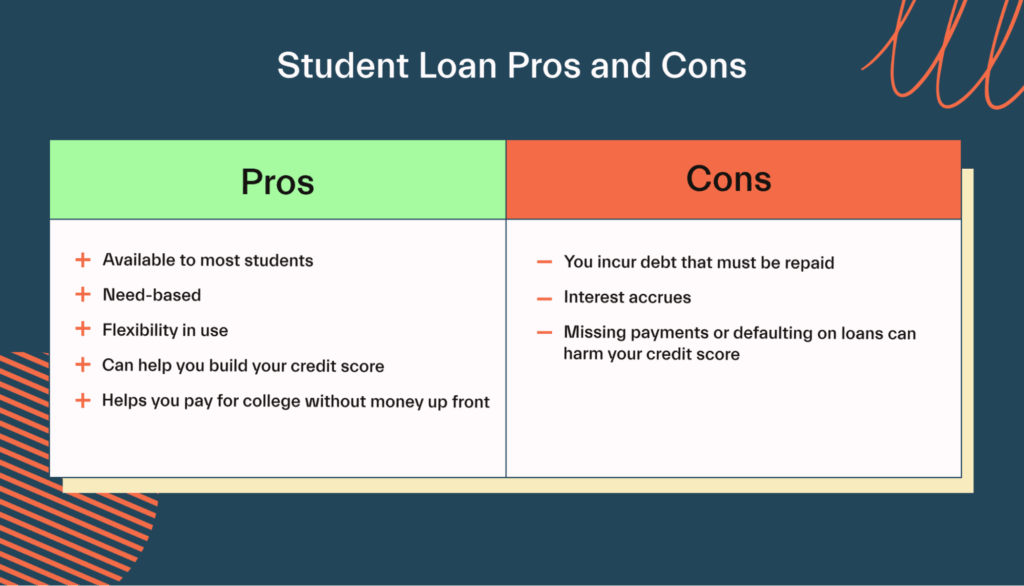
The fundamental difference lies in repayment obligation. Scholarships, grants, and bursaries are forms of financial aid that do not need to be repaid, typically awarded based on academic merit, financial need, or specific talents and affiliations. Loans, on the other hand, are borrowed funds that must be repaid, often with interest accumulating over time. This repayment obligation adds a financial burden to graduates, potentially affecting their future financial planning.
How Do Scholarships Impact Future Financial Stability?
Scholarships significantly enhance future financial stability by reducing or eliminating the need for loans. Less debt upon graduation translates to increased disposable income, allowing graduates to pursue their career goals without being burdened by hefty monthly loan payments. This can improve their ability to save for a down payment on a house, invest in retirement, or pursue further education without financial strain.
What are the Different Types of Loans Available for Education?
Educational loans broadly fall into two categories: federal and private. Federal loans are offered by the government and typically come with fixed interest rates and flexible repayment options, including income-driven repayment plans. Private loans are offered by banks and other financial institutions and may have variable or fixed interest rates. Private loans often require a credit check and may not offer the same protections as federal loans, such as deferment or forbearance during periods of economic hardship.
What Factors Should I Consider When Choosing Between Scholarships and Loans?
When deciding between scholarships and loans, consider your financial need, academic record, and eligibility for various scholarship programs. Prioritize applying for scholarships and grants as the primary source of funding. If scholarships do not cover all expenses, carefully evaluate loan options, focusing on interest rates, repayment terms, and potential for deferment or forbearance. Consider your anticipated future income and carefully estimate your ability to comfortably manage loan repayments.
How Can I Maximize My Chances of Receiving Scholarships?
To increase your chances of securing scholarships, start early and research extensively. Identify scholarships aligned with your academic profile, extracurricular activities, and personal background. Craft compelling essays and personal statements highlighting your achievements and goals. Seek recommendations from teachers and mentors who can attest to your abilities and potential. Apply for as many scholarships as possible to improve your odds of receiving funding.
| Feature | Scholarships | Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Repayment | Not Required | Required with Interest |
| Source | Grants, Organizations, Institutions | Government, Banks, Credit Unions |
| Eligibility | Merit, Need, Specific Criteria | Creditworthiness, Enrollment Status |
| Impact on Future Finances | Positive (Less Debt) | Potentially Negative (Debt Burden) |
| Risk | Low (No Repayment) | High (Repayment Obligation) |
Are scholarships better than loans?
Financial Burden and Long-Term Impact
- The most significant advantage of scholarships is the reduction of long-term debt. Graduating with less debt or no debt at all provides more financial flexibility in the future, allowing individuals to pursue career goals, invest in their future, or purchase a home without the burden of significant loan repayments.
- Loans, on the other hand, come with interest rates that can accumulate over time, significantly increasing the amount to be repaid. This can impact credit scores and limit financial opportunities for years to come.
- Choosing scholarships over loans will always be more economical long-term.
Eligibility and Competition
- Securing scholarships can be competitive, as they are often based on merit, talent, or specific criteria. Students need to invest time and effort in researching and applying for various scholarship opportunities. The application process may involve essays, interviews, and providing evidence of academic achievements or extracurricular involvement.
- Loans, especially federal student loans, are often easier to obtain as eligibility is typically based on financial need and enrollment status. However, private loans can have stricter credit requirements, potentially posing a barrier for some students.
- The availability of scholarships is limited compared to the availability of loans. The application process is highly competitive and requires diligence.
Impact on Credit Score and Financial Freedom
- Taking out student loans can immediately impact your credit score. While federal student loans typically don't require a credit check, private student loans do, and a high credit score is often required for a lower interest rate.
- Loans require monthly payments that can strain a graduate's budget, delaying other financial goals. Scholarships provide financial freedom from the outset, allowing graduates to focus on career advancement and wealth-building.
- The absence of loan repayments frees up resources for other important life investments.
Types and Conditions of Aid
- Scholarships often come with specific requirements, such as maintaining a certain GPA or participating in specific activities. Failing to meet these requirements could result in the loss of the scholarship. It is important to carefully review the terms and conditions before accepting a scholarship.
- Loans typically have more flexible repayment options, including income-driven repayment plans and deferment or forbearance options. However, these options may extend the repayment period and increase the total interest paid. Loans give the flexibility of adjusting the payment based on circumstances.
- Both scholarships and loans can be categorized based on the type of institution offering them. Understanding these differences is essential for effective financial planning.
Long-Term Cost vs. Immediate Accessibility
- While scholarships are undeniably more beneficial in the long run due to the absence of repayment obligations, loans can provide immediate access to funds, enabling students to pursue education when scholarships are insufficient or unavailable. Loans can be more readily accessible when immediate funding is needed.
- The long-term cost of loans can be significant, especially with accruing interest. Students should carefully consider the total repayment amount before taking out a loan. A good strategy is to minimize the use of loans and search for every available scholarship possible.
- A carefully considered combination of both, where scholarship efforts are prioritized, can be an effective strategy for managing educational expenses. Balancing the two could be the key to a debt free future.
Is financial aid better than student loan?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Private-vs-Federal-College-Loans-Whats-the-Difference-31c92251f6b243e3b1e4bba3b5612791.jpg)
Grant vs. Loan: Immediate Cost Impact
The primary distinction lies in the immediate financial burden. Grants, scholarships, and work-study programs offer "free" money, reducing the amount students need to borrow upfront. Loans, conversely, add to the immediate financial need and create a future repayment obligation. The long-term benefits of grants and scholarships are very clear; students can have a larger income over time.
- Grants and scholarships decrease the up-front cost of attending college.
- They do not accrue interest or require repayment.
- This lowers the amount of debt a graduate needs to worry about after college.
Debt Burden and Long-Term Financial Health
Student loans, while helpful in the short term, create a significant long-term debt burden. This debt can affect major life decisions such as buying a home, starting a family, or pursuing further education. Relying heavily on loans can also limit career choices, as graduates may feel pressured to choose high-paying jobs to manage their loan repayments.
- High debt-to-income ratio can make one's finances suffer more greatly.
- Student loans could require high monthly payments.
- Loan payments could make buying property more difficult.
Eligibility Requirements and Accessibility
Both financial aid and student loans have eligibility requirements, but the criteria differ. Financial aid is often needs-based or merit-based, and some students may not qualify. Federal student loans are generally more accessible to a wider range of students, regardless of their financial situation, but interest rates and loan terms can vary. The loan qualification depends on credit, and income requirements from the parents.
- Financial aid eligibility often depends on financial need or academic achievement.
- Federal student loans are generally more accessible than private loans.
- Loan terms and interest rates can vary widely.
The Role of Interest Rates and Repayment Terms
Student loans come with interest rates, which increase the overall cost of borrowing. The type of loan (federal or private) and the borrower's creditworthiness affect the interest rate. Repayment terms also vary, impacting the monthly payment amount and the total repayment period. Lower interest rates and flexible repayment options can make loans more manageable, but it's crucial to understand the long-term implications.
- Federal loans generally have fixed interest rates.
- Private loans may have variable interest rates, subject to change.
- Repayment options can include income-driven repayment plans.
Combining Aid and Loans for Optimal Affordability
The most effective strategy often involves combining financial aid and student loans. Prioritizing grants and scholarships minimizes the need for borrowing, and strategic use of loans can fill the remaining funding gap. It's important to explore all available financial aid options before resorting to loans and to borrow only what is absolutely necessary.
- Complete the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) to apply for federal aid.
- Research and apply for scholarships from various sources.
- Explore work-study opportunities to earn money while attending school.
Frequently asked questions
What is the primary difference between scholarships and loans?
Scholarships are a form of financial aid that you do not have to repay, typically awarded based on merit, need, or specific criteria. In contrast, loans are borrowed money that must be repaid with interest over a set period, creating a debt obligation for the borrower.
What are the advantages of choosing scholarships over loans?
The most significant advantage is that scholarships reduce the overall cost of education because you don't have to pay them back. This means less financial burden after graduation, allowing you to pursue career opportunities or other goals without the pressure of debt repayment. Pursuing scholarship opportunities can also improve one's academic background.
When might taking out student loans be necessary?
Student loans might be necessary when scholarships and grants are insufficient to cover the full cost of tuition, living expenses, and other educational fees. They can also be crucial if you don't qualify for enough scholarships or if you need to attend a more expensive program to achieve your career aspirations. Also, loans are much more readily available than some scholarships.
How can I maximize my chances of securing scholarships and minimizing my need for loans?
To maximize scholarship opportunities, start early and apply widely to as many scholarships as possible that you are eligible for. Focus on improving your academic record, participate in extracurricular activities, and craft compelling application essays that showcase your strengths and goals. Also, consider attending a more affordable school to lower overall costs, decreasing the dependence on loans.
